Introduction:
With the continuous advancement of technology and the rapid evolution of lighting techniques, the photocell, as a pivotal lighting control device, is becoming an indispensable component in both architectural and public spaces.
However, when selecting a light controller, cost is a crucial factor to consider alongside its performance and functionalities. Understanding the mechanisms behind the formation of light controller costs requires an in-depth exploration of various factors, ranging from technical specifications to market competition, and from material selection to regulatory compliance.
This article will delve into several key factors influencing the cost of light controllers, aiming to provide consumers, industry professionals, and decision-makers with a clear understanding, enabling them to make informed decisions in choosing lighting solutions.
Through this exploration, we will uncover the intricate cost structure behind light controllers and offer valuable insights into the future trends of light control technology.
Factors affecting the cost of light controllers
1.Raw materials and manufacturing processes
The cost of light controllers is directly influenced by both their raw materials and manufacturing processes. These two aspects, while shaping the performance and reliability of light controllers, also have a significant impact on their overall costs.
Firstly, the choice of raw materials directly determines the quality and durability of light controllers. High-quality raw materials typically ensure the long-term reliable operation of light controllers, while also reducing maintenance and replacement costs. Factors such as weather resistance, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance need to be thoroughly considered when selecting raw materials, as they directly relate to the operational lifespan of light controllers in various environments.
Secondly, the sophistication and efficiency of manufacturing processes also greatly shape the ultimate cost of light controllers. Adopting advanced manufacturing technologies and equipment can enhance production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and, to a certain extent, minimize overall costs. Moreover, efficient manufacturing processes contribute to ensuring product consistency and stability, reducing defect rates, thus further saving costs.
In summary, the raw materials and manufacturing processes of light controllers not only directly impact product quality and performance but also to some extent determine the production and maintenance costs. Therefore, manufacturers need to strike a balance between quality, reliability, and cost when selecting raw materials and manufacturing processes, ensuring that light controllers offer a competitive cost-effectiveness in the market.
- Technical Specifications and Performance:
The technical specifications and performance of light controllers are crucial factors directly influencing their costs. The excellence in these aspects not only determines the practicality of light controllers but also has profound implications for their manufacturing and maintenance costs. Below, we will primarily analyze three aspects: voltage, surge protection, and zero-crossing technology.
Voltage:
Light controllers typically need to adapt to different voltage conditions based on the characteristics of various markets and power systems. Voltage standards and frequencies may differ in different regions and applications, necessitating the design of light controllers to accommodate these variations. Typical voltage configurations include, but are not limited to:
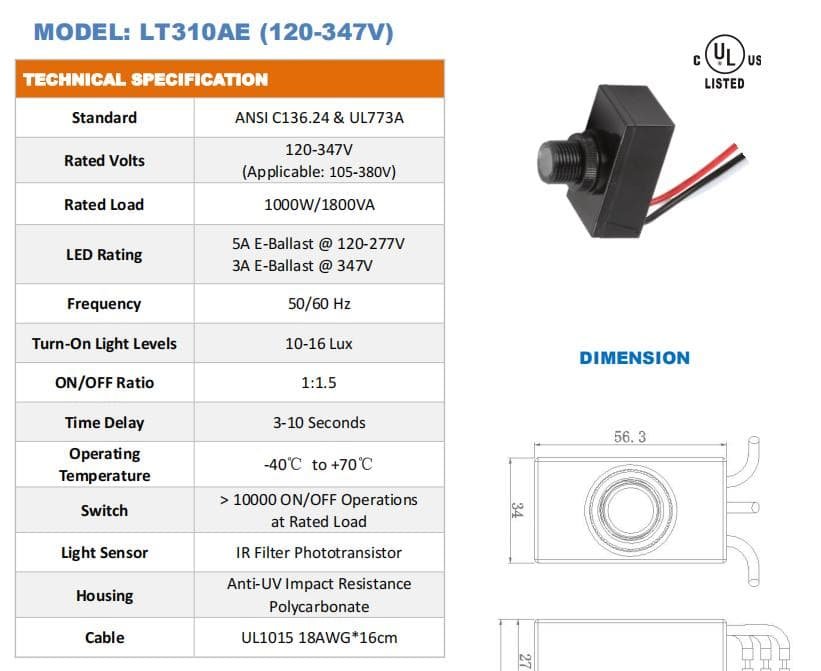
120VAC: Common residential and commercial electrical standard in North America and some other regions.
240VAC: Standard voltage for homes and businesses in certain regions, especially in Europe.
12-48VDC: Required for specific applications, such as solar lighting systems or devices powered by low-voltage direct current (DC).
120-277VAC: Common range for commercial and industrial power in North America.
347-480VAC: Higher voltage range used in some industrial and commercial applications.
Different voltage situations necessitate different specifications for electronic components, such as relays, resistors, capacitors, and inductors, to ensure the safe and reliable operation of light controllers in various power systems. Additionally, these varying voltage specifications may impact the design costs of light controllers, as the specifications and prices of corresponding electronic components may differ. Therefore, considering and adapting to different market voltage conditions is crucial in the design and production of light controllers.
Surge protection is a technology used to safeguard electronic devices and power systems from voltage surges, current surges, and electromagnetic interference.
Surges are rapid increases in voltage or current that typically result from events like lightning strikes, power grid faults, power switch operations, or the switching of inductors or capacitors. This sudden fluctuation in voltage or current can cause severe damage to equipment, shorten its lifespan, or even lead to fires.
In the mentioned markets and applications, particularly in lighting systems, outdoor lighting, building automation, industrial control, and traffic signal lights, surge protection may be required for light controllers.
Although adding this feature increases costs, this preventive measure ensures the stability of light controllers and their connected devices when facing voltage and current surges, thus maintaining essential aspects such as electrical safety and device reliability.

Zero-Crossing Technology:
Zero-crossing technology is a specialized technique used to control lighting devices. It aims to reduce current spikes and minimize electromagnetic interference by performing control operations at the zero-crossing point of the power supply voltage.
This technology helps improve the efficiency of lighting systems, extend device lifespans, and reduce the burden on the power grid. Introducing zero-crossing technology may increase the initial cost of light controllers to some extent.
This is because zero-crossing technology requires more advanced electronic components and control logic to ensure accurate switching operations at the zero-crossing point of the power supply voltage. While introducing zero-crossing technology may increase the initial cost of light controllers, this investment typically brings some significant long-term advantages, such as:
System Performance Improvement: Zero-crossing technology helps improve system performance, including reducing current harmonics, minimizing electromagnetic interference, and enhancing power factor.
Extended Device Lifespan: Smooth switching operations can reduce the impact on devices during switching, helping extend the lifespan of lighting equipment.
Increased Energy Efficiency: Zero-crossing technology contributes to higher energy efficiency, reducing energy waste and potentially lowering operational costs in the long run. Therefore, although introducing new technology may incur some initial costs, these costs may be offset in the long term by performance enhancements and reduced maintenance costs.
In conclusion, the technical specifications and performance of light controllers require careful consideration in determining their costs. Manufacturers must prudently weigh the relationship between costs and benefits at different performance levels and technical specifications to ensure that light controllers possess advanced technological features and competitive prices in the market.
- Protection Rating(IP67 ,IK09 etc.) and Durability
The protection rating and durability of light controllers are crucial factors influencing their costs. These aspects directly relate to the lifespan, stability, and reliability of light controllers in different environments. Here are their impacts on costs:
Protection Rating:
High Protection Rating Requirements: If light controllers need to operate in harsh environments, such as outdoors, humid, or dusty locations, a higher protection rating like IP65 or IP66 IP67 may be required. This may involve the use of waterproof and dustproof materials, as well as sealed designs, increasing manufacturing costs.

Additional Sealing and Material Costs: Achieving a high protection rating often necessitates the use of special sealing materials, waterproof connectors, and coatings. These additional materials and processes may contribute to increased manufacturing costs.
Stringent Testing and Certification: Attaining a high protection rating requires more rigorous testing and certification to ensure compliance with relevant standards. This may increase the costs associated with quality control and testing.
Durability:
Impact on Lifespan: The durability of light controllers directly impacts their lifespan. If designed for long-term reliable operation, more durable materials and components may be required, potentially raising costs.
High-Quality Manufacturing: Long-term durability often demands higher-quality manufacturing standards, involving more precise processes and stricter quality control, which could lead to cost escalation.
Costs of Durability Testing: To ensure product durability, additional durability testing may be necessary, adding to the costs of testing and validation.
While enhancing protection rating and durability typically increases manufacturing costs, it also expands the potential applications and extends the lifespan of light controllers. This may result in lower overall ownership costs over the long term. During the design phase, manufacturers often consider the intended use of the product, market demands, and user performance expectations to ensure that light controllers meet specific requirements while maintaining reasonable costs.
- Regulations and Certification Requirements
The regulations and certification requirements for light controllers have direct and indirect impacts on their costs. Different regions and markets may have varying regulatory and certification standards, and light controller manufacturers need to adhere to these standards to ensure product compliance. Here are the primary influences of these regulations and certifications on the costs of light controllers:
Testing and Certification Costs:
Compliance Testing Expenses: Light controller manufacturers need to conduct various compliance tests to ensure their products meet the regulatory and certification requirements of specific regions or markets. These tests involve aspects such as performance, electromagnetic compatibility, protection ratings, etc., incurring relatively high costs.
Certification Agency Fees: Certification agencies associated with compliance testing may charge fees, and manufacturers need to cover these costs to obtain the relevant certifications.
Design and Engineering Costs:
Regulation-Conforming Design: Manufacturers may need to invest more resources in the product design phase to ensure compliance with specific regulations and standards from the outset. This may involve using specific materials, adopting special designs, thereby increasing design costs.
Preparation of Technical Documents: Submitting technical documents to certification agencies is part of obtaining certification. Manufacturers need to allocate additional time and resources to prepare and submit these documents.
Manufacturing and Quality Control Costs:
Compliance in Production Processes: Maintaining compliance of the production process with certification requirements may necessitate additional control measures and monitoring. This could include stricter quality control, record-keeping, bringing about additional production costs.
Use of Compliant Materials: Meeting certification requirements typically demands the use of specific compliant materials, which may be more expensive than non-compliant alternatives.
Market Entry:
Advantages of Market Expansion: Light controllers with compliance certifications can more easily enter specific markets, as many markets require products to meet certain standards. This may result in increased market share and more business opportunities, partially offsetting the costs of certification.
While regulations and certification requirements may increase the manufacturing costs of light controllers, they also provide assurances of product quality and performance. They help manufacturers establish trust and reputation in competitive markets. When making decisions, manufacturers often need to balance the costs of compliance with the long-term benefits of market access, sustainability, and customer trust.
- Customization Requirements:
Customization requirements for light controllers typically result in a series of cost implications. Here are some potential cost changes that may arise due to customization demands:
Design and Engineering Costs:
Customized Design: Customer customization often requires specialized design work to meet unique requirements. This may include circuit design, aesthetic design, and functionality customization. Associated design and engineering costs will increase.
Material Selection:
Special Materials: Customers may request the use of special materials, which could be more expensive than conventional materials. This involves an increase in raw material costs.
Production Process Adjustments:
Special Processes: If customization demands necessitate adjustments to the production process or the adoption of special manufacturing methods, this may lead to production line adjustments and process optimization, increasing production costs.
Handcrafted Customization: Some customization requirements may not be met through automated production and may require more manual operations, reducing production efficiency and increasing costs.
Small-Batch Production:
Customization often involves small-batch production: Customization typically involves production in small batches, unlike mass production that can achieve cost efficiency. Production and handling for each custom order may consume more time and resources.
Testing and Quality Inspection:
Additional Testing: Custom products may require additional testing to ensure they meet the customer’s specific requirements. This may include validation of custom features and performance testing, increasing testing costs.
Quality Inspection Standards: Custom products usually need to adhere to higher quality inspection standards to ensure their quality. This may require more resources for inspection and quality assurance.
Delivery and Services:
Special Packaging and Delivery: Custom products may require special packaging and delivery methods to ensure they are not damaged during transportation. This may result in additional packaging costs and logistics expenses.
Customer Service: Custom products may require more customer service, including technical support and communication regarding customization requirements, increasing operational costs.
Customization requirements tend to present additional cost challenges. For instance, special casing designs, customized sensing parameters, or other bespoke features often require additional engineering design and production processes, leading to higher prices for customized versions of light controllers. Custom products generally demand more resources and labor, hence their prices may be influenced by the degree of customization.
- Technological Innovation:
Indeed, new technological innovations or improvements often have an impact on the manufacturing costs and performance of a product, subsequently leading to changes in the price tag. Here are some factors that might contribute to the price variation of next-generation photovoltaic products:
Material Technology Innovations:
Application of New Materials: Introducing more advanced and efficient materials can enhance the performance of photovoltaic cells, improving energy conversion efficiency. This could result in changes in raw material costs, thus influencing manufacturing costs and the final product price.
Production Process Improvements:
Efficient Production Techniques: The introduction of new production processes and manufacturing technologies may increase production efficiency, reducing production time and costs. This can have a positive impact on the manufacturing costs and price of the product.
Material Technology Innovations:
Application of New Materials: Introducing more advanced and efficient materials can enhance the performance of photovoltaic cells, improving energy conversion efficiency. This could result in changes in raw material costs, thus influencing manufacturing costs and the final product price.
Production Process Improvements:
Efficient Production Techniques: The introduction of new production processes and manufacturing technologies may increase production efficiency, reducing production time and costs. This can have a positive impact on the manufacturing costs and price of the product.
In general, new technological innovations or improvements often affect the manufacturing costs and performance of photovoltaic products, thereby influencing product prices. This is why next-generation products typically come with different price tags when introduced to the market. Consumers and industry participants need to pay attention to technological advancements to understand the performance and pricing characteristics of new products and make choices that align with their needs and budgets.
- Supply Chain Issues:
Supply chain issues in photovoltaic cell manufacturing, such as the stability of raw material supply and problems during the production process, can potentially cause price fluctuations.
Changes in raw material prices directly impact the manufacturing costs of photovoltaic components, subsequently affecting product prices. The following are the primary impacts of fluctuations in raw material prices on the prices of photovoltaic components:
Increase in Hardware Costs:
Photovoltaic Components: Photovoltaic controllers typically include light-sensitive components like photoresistors or photodiodes. If the raw material prices for these components rise, the hardware costs for manufacturers will increase.
Electronic Components: Other electronic components such as capacitors, resistors, etc., may also be influenced by fluctuations in raw material prices.
Enclosure and Materials:
Plastics and Metals: The enclosure of photovoltaic controllers is usually made of plastic or metal materials. An increase in raw material prices may lead to an escalation in the manufacturing costs of the enclosure.
Optical Components:
Lenses and Filters: Optical components like lenses and filters in photovoltaic controllers may be affected by fluctuations in the prices of materials such as glass, plastic, or other substances.
Circuit Boards and Connectors:
Circuit Boards: If specialized materials are used for the circuit boards in photovoltaic controllers, changes in raw material prices can impact the manufacturing costs of these boards.
Connectors and Wires: Price increases in connectors and wires can also have a certain degree of impact on the overall product costs.
Production Processes and Auxiliary Materials:
Printing and Assembly Materials: The production of photovoltaic controllers may require various materials for printing and assembly, including inks, adhesives, etc. Fluctuations in the prices of these materials can also impact costs.
Environmentally Friendly and Safety Materials: Materials complying with environmental and safety standards might be more expensive, potentially increasing the manufacturing costs of the product.
- Packaging and Accessories:
The packaging and accessories of a light controller have direct and indirect impacts on the manufacturer’s costs, involving various aspects such as production, transportation, marketing, and customer experience. High-quality, specially designed, or materials-specific packaging and accessories usually result in increased costs.
Additional Components: Some models of light controllers may require additional components, such as special mounting brackets, connecting cables, or controllers. The manufacturing costs of these accessories need to be taken into account.

Customized Accessories: If there are customized requirements for accessories due to customer demands, manufacturers may have to bear additional customization costs.
Standardization and Universality: Designing accessories with high universality can contribute to lowering manufacturing costs, as they can be shared across multiple product models.
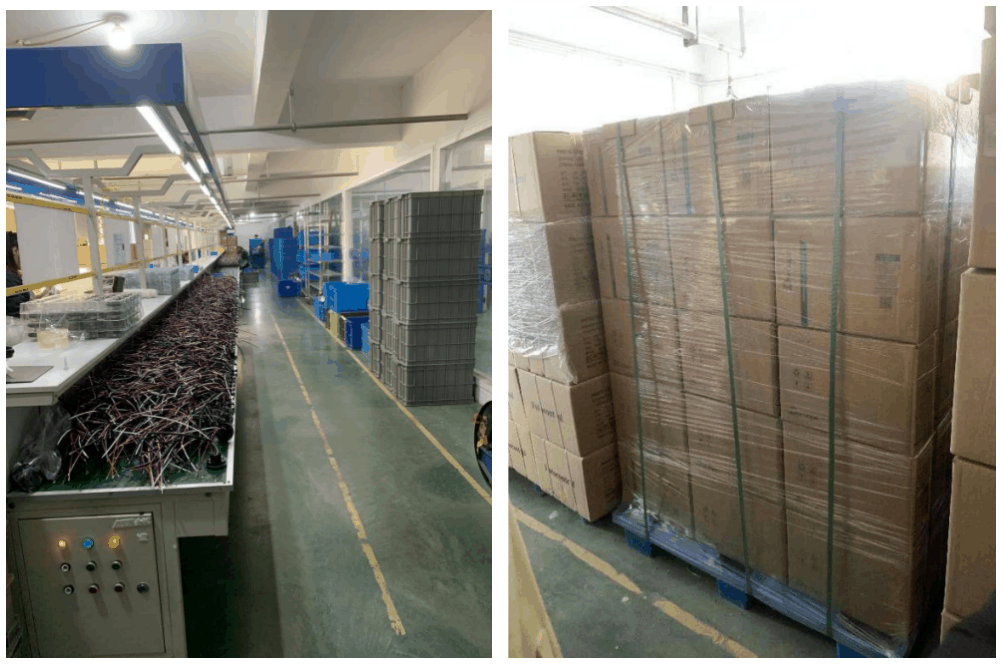
- Production Batch:
The production batch of light controllers significantly influences prices, often manifested in the cost benefits brought about by batch production. Here are some key factors affecting the prices of light controllers due to production batch

Fixed Cost Allocation:
Large-scale Production: When light controllers are produced on a large scale, fixed costs (such as equipment depreciation, factory rent, etc.) can be spread across more products, reducing the fixed cost per unit.
Small-scale Production: Conversely, small-scale production may result in less fixed cost allocation, making the fixed cost per unit relatively high.
Raw Material Procurement Cost:
Batch Purchasing Advantage: Large-scale production usually allows for larger purchase volumes, enabling discounts or more favorable agreements for raw material procurement. Manufacturers can negotiate with suppliers more effectively and benefit from economies of scale.
Small-scale Production: In small-scale production, raw material procurement costs may be relatively high, as the advantages of bulk purchasing cannot be fully utilized.
Production Efficiency:
Large-scale Production: With an increase in production scale, production lines and workflows can be optimized, enhancing production efficiency. The application of automation and standardization can reduce labor and production cycle costs.
Small-scale Production: Smaller production scale may lead to a decrease in production efficiency because of limited fixed cost allocation. The production process may be more manual, resulting in increased production costs per unit.

Quality Control Cost:
Large-scale Production: In large-scale production, manufacturers can more easily implement stringent quality control standards, improving product quality through automation and advanced inspection equipment. This helps reduce defect rates and maintenance costs.
Small-scale Production: In small-scale production, quality control may require more manual operations, increasing the cost of quality control.

In general, large-scale production often brings lower unit product costs due to the various cost benefits of increased production scale. However, achieving large-scale production may require greater capital investment and more complex management. Manufacturers need to carefully balance costs and benefits and choose the production scale that suits their business model.
- Currency Exchange Rates and Raw Material Prices:
Currency exchange rates and raw material prices are two interrelated factors that have a significant impact on the costs and profitability of businesses.
Currency Exchange Rates:
Exchange Rate Fluctuations: The exchange rate is an indicator of the relative value between two different currencies. When businesses purchase raw materials from abroad or sell products in foreign markets, fluctuations in exchange rates directly affect transaction costs and revenue.
Import Costs and Export Revenue: If a business needs to import raw materials, the depreciation of the currency of the trading partner country may lead to an increase in raw material costs. Conversely, if selling products to other countries, the depreciation of that country’s currency may enhance the product’s competitiveness in the international market but could reduce the actual value of export revenue.
Foreign Exchange Risk: Exchange rate fluctuations also introduce foreign exchange risk. Businesses may adopt various strategies, such as forward contracts or financial instruments, to manage this risk.
Raw Material Prices:
Global Market Supply and Demand: The prices of raw materials are influenced by global market supply and demand dynamics. Shortages in supply or increased demand may result in rising raw material prices, while oversupply may lead to price declines.
Geopolitical and Natural Factors: Geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and other factors can impact the production and supply chain of raw materials. These factors may contribute to price volatility.
Inflation: Inflation is also one of the factors affecting raw material prices. Inflation can lead to increased production costs, thereby driving up raw material prices.
The relationship between these two factors is evident in how businesses engaged in international trade must closely monitor fluctuations in currency exchange rates, as this directly impacts their procurement and selling costs. Additionally, changes in the global raw material market affect production costs and product prices. Businesses need to consider these factors comprehensively and adopt flexible strategies to adapt to the ever-changing market environment, ensuring competitiveness and profitability.
- After-Sales Service and Warranty:
Some manufacturers may offer more comprehensive after-sales service and longer warranty periods, which can lead to an increase in product prices
Costs of Warranty Policies:
Service Personnel Training and Expenses: Providing excellent after-sales service often requires training service personnel to ensure they can effectively address customer issues and provide viable solutions. This involves training costs, wage expenditures, and other related expenses.
Warranty Duration and Conditions: The manufacturer’s warranty policy includes the warranty period and specific warranty conditions. Offering longer warranty periods or more lenient warranty conditions may increase maintenance and replacement costs.
Costs of Replacement Products and Parts: If manufacturers provide replacement products or free replacement parts during the warranty period, it adds to the cost of after-sales service. This may include producing additional parts, transportation costs, and potential lost sales opportunities.
Quality Control After Warranty Service: Products repaired under warranty need to undergo quality control to ensure they meet the manufacturer’s quality standards. This may require additional time and resources, thus increasing costs.
Providing high-quality after-sales service and competitive warranty policies are often considered crucial factors for brand loyalty but simultaneously increase the operational costs for manufacturers. Manufacturers need to find a balance between delivering a high level of after-sales service and warranty policies to meet customer expectations while maintaining sustainable operations.
- Brands and Manufacturers:
Products from well-known brands or those with a strong manufacturing track record typically come with higher prices. The reputation of the brand and the credibility of the manufacturer significantly impact the pricing.
Quality Assurance:
High Brand Reputation: Renowned brands are often known for their commitment to quality and high standards. This means they may use higher-quality materials, advanced manufacturing processes, and stricter quality control standards to ensure product stability and reliability.
Manufacturer’s Credibility: Manufacturers with a good track record and solid reputation tend to prioritize the manufacturing process and implement rigorous quality control measures. This can reduce defect rates during manufacturing and improve overall product quality.
Research and Innovation Costs:
Brand Reputation and R&D: Well-known brands typically invest more resources in research and development (R&D) to introduce advanced products. This may result in higher R&D costs but also endows the product with advanced features and performance.
Manufacturer’s Credibility and Technological Expertise: The credibility of a manufacturer is closely tied to its technological expertise. Manufacturers with a good reputation may have more expertise in technological research and development, contributing to higher technical content in products but potentially leading to higher R&D costs.
Conclusion
In this article, we delve into several key factors influencing the cost of light controllers, revealing the intricate cost structure behind this lighting control device.
In terms of technical specifications and performance, elements such as sensing range, sensitivity, and response time have a direct and significant impact on the cost of light controllers.
Regarding customization requirements, special designs and functional demands may lead to the production of customized versions, thereby affecting the overall cost. The quality of raw materials and manufacturing processes is crucial for the performance and lifespan of light controllers, directly influencing manufacturing costs.
Market supply and demand and the competitive environment determine the market pricing of light controllers, exerting an indirect but sustained influence on costs. Regulatory standards and certification requirements may add additional costs to the manufacturing process, but they are necessary steps to ensure product compliance and quality.
Considering these factors comprehensively, the cost of light controllers not only reflects the expenses associated with their manufacturing and production but is also influenced by technological innovation, market trends, brand competition, and regulatory environments.
Understanding these factors assists consumers, industry professionals, and decision-makers in making informed decisions when selecting appropriate lighting solutions. In the future, as technology advances and the market evolves, the dynamic changes in the cost of light controllers will continue to be shaped by these factors, bringing more innovation and possibilities to the lighting industry.







