Introduction
In the realm of energy efficiency and smart lighting solutions, photocontrols have become key components. These devices, which control lighting based on ambient light levels, offer significant energy savings and automation benefits. A frequently asked question is whether photocontrols can truly achieve 0V in standby mode. Let’s delve into this technical issue.
Photocontrols
Photocontrols, or photocells, are sensors that detect light levels and switch electrical devices accordingly. They are widely used in streetlights, outdoor lighting, and various automated applications. The main advantage of photocontrols is their ability to reduce energy consumption by ensuring lights are only on when needed.
Standby Power Consumption
Standby power consumption refers to the electricity used by electronic devices when they are turned off or in standby mode. Achieving a 0V standby state means the device would consume no power when not in use.
Can 0 Power Consumption Be Achieved?
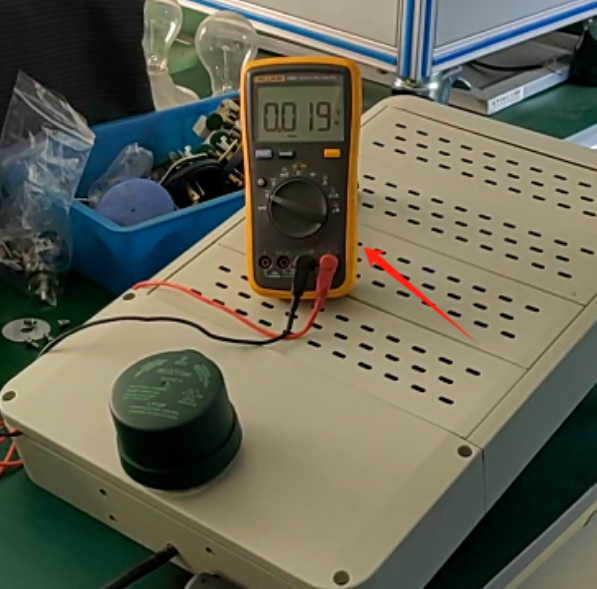
In reality, achieving 0V standby in photocontrols is extremely challenging.
Despite advancements in photocontrol technology that have significantly reduced power consumption—such as the photocontrols from Zhejiang lead-top Electric Co., Ltd., which can keep power consumption to ≤ 0.5 watts at 120VAC.
These circuits typically require a small amount of power to continuously monitor ambient light changes, even when the controlled devices (like lights) are off. Thus, reaching a true 0V is difficult.

Although photocontrols cannot achieve a 0V standby state, they usually consume minimal power, typically in the milliwatt range. This small consumption is necessary to maintain the functionality of the internal circuitry.
Practical Implications
Energy Efficiency:
While the concept of a 0V standby state is appealing, modern photocontrols consume very low power in standby mode, contributing negligibly to overall energy usage. The energy savings from the efficient operation of photocontrols far outweigh their standby power consumption. Turning off streetlights completely to save the tiny amount of standby power would hinder the photocontrols’ ability to detect light changes and automatically manage lighting, which could be inconvenient.
Technological Advancements:
Ongoing research and technological advancements aim to further reduce standby power consumption. Innovations in low-power electronics and smart energy management systems hold promise for designing even more efficient photocontrols in the future.
Conclusion
Achieving a true 0V standby state in photocontrols remains an ideal rather than a current reality. However, the small amount of power these devices consume in standby mode is a minor trade-off for the significant energy savings and automation benefits they provide.
With ongoing advancements, we can expect further improvements in the efficiency and power consumption of photocontrols, bringing us closer to the ideal of zero standby power consumption.
Zhejiang lead-top Electric is committed to continually improving and optimizing photocontrol products, driving advancements in efficient and eco-friendly technologies, and providing the best solutions for our customers.








