Introduction
Light is an indispensable part of our lives, providing not only visibility but also influencing our emotions and quality of life. In modern society, lighting systems are no longer just about providing brightness; they are a key component capable of creating a comfortable, safe, and intelligent environment.
With the advancement of technology, sensor technology is assuming an increasingly crucial role in the field of lighting. It not only enhances energy efficiency but also elevates user experiences, thereby making lighting systems more intelligent and environmentally friendly. This article will delve into the diverse applications of sensor technology in both indoor and outdoor lighting, covering infrared sensors, ultrasonic sensors, and microwave sensors for indoor lighting, as well as photocells, infrared sensors, and sound sensors for outdoor lighting.
Sensors Applicable in Indoor Lighting
A. Infrared Sensors
Working Principle:
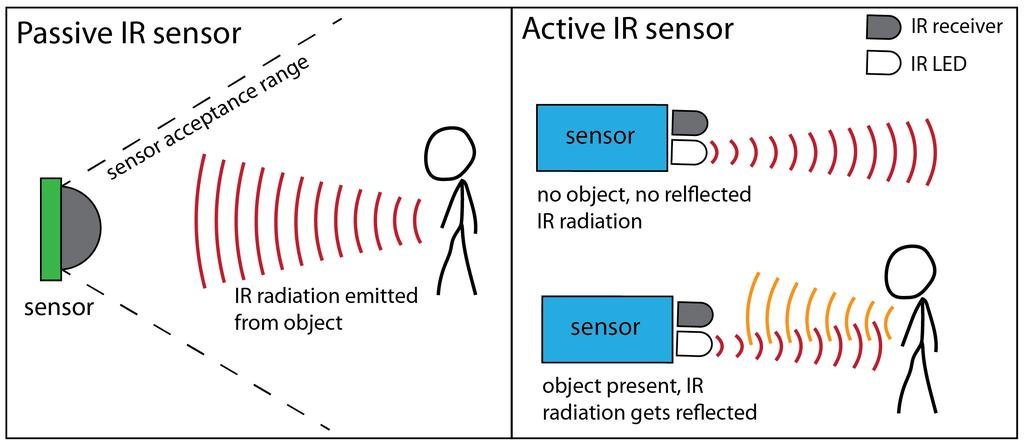
Infrared sensors detect changes in the surrounding environment by sensing the infrared radiation emitted by the human body. When an object enters the detection range, the infrared sensor perceives the change in radiation and triggers corresponding actions, such as turning lighting devices on or off.
B. Ultrasonic Sensors
Working Principle:
Ultrasonic sensors emit ultrasonic waves and measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back, calculating the distance of objects to the sensor. When an object moves or enters the detection range, the ultrasonic sensor can quickly respond.
C. Microwave Sensors
Working Principle:
Microwave sensors emit microwave radiation and receive its reflected signal. By analyzing changes in the signal, the sensor determines the position and movement status of objects.
Advantages:
Instant Response: Infrared sensors achieve millisecond-level response times, allowing lighting systems to adapt to environmental changes promptly.
High Sensitivity: Capable of detecting subtle movements, ensuring appropriate lighting levels within the human activity range.
Energy Efficiency: Infrared sensing technology helps reduce energy consumption by promptly turning off unused lighting devices, contributing to energy-saving and environmental goals.
Precision Positioning: Achieves precise sensing of object positions, providing finer control for directional lighting.
Insensitive to Light Conditions: Unaffected by changes in lighting, suitable for various indoor environments, whether bright or dim.
Wide Range of Applications: Suitable for large open indoor areas such as offices, exhibition halls, meeting diverse needs in different scenarios.
Smart Lighting Control: Indoor sensors can detect human activity, enabling intelligent lighting control. When someone enters a room, the sensor can automatically turn on the lights and turn them off when the person leaves, improving energy efficiency and convenience.
Enhanced Safety: During nighttime or low-light conditions, indoor sensors can trigger the lighting system, enhancing indoor safety and preventing accidental collisions or falls.
Integration into Smart Homes: Indoor sensors can integrate with other smart home devices, such as smart temperature control and security systems, achieving comprehensive smart home control and scenario linkage.
Comfortable Experience: By real-time sensing of human activity, indoor sensors can adjust parameters like lighting and temperature, providing a more comfortable living experience.
Applications:
Office: In offices, infrared sensors enable intelligent lighting control in workstations, enhancing work efficiency.
Shopping Mall: In shopping malls, infrared sensors can control lighting in aisles and common areas, improving the shopping experience.
Healthcare Facilities: In healthcare institutions, infrared sensors can be used for intelligent lighting in patient rooms, corridors, ensuring comfort for patients and staff.
Sensors Applicable in Outdoor Lighting
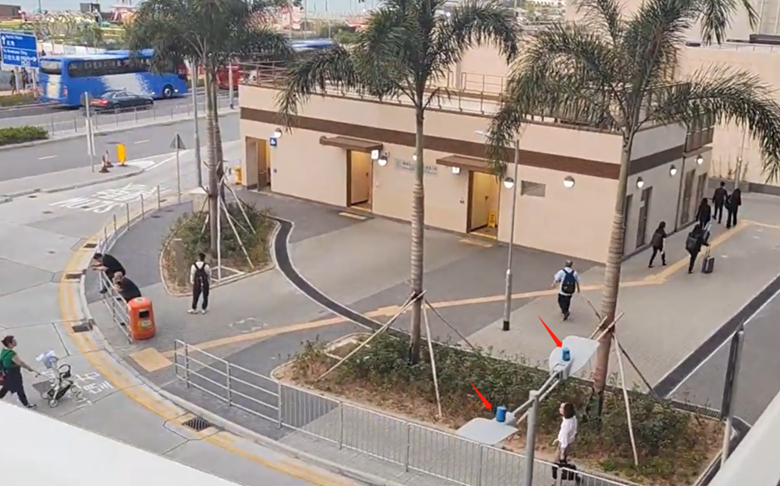
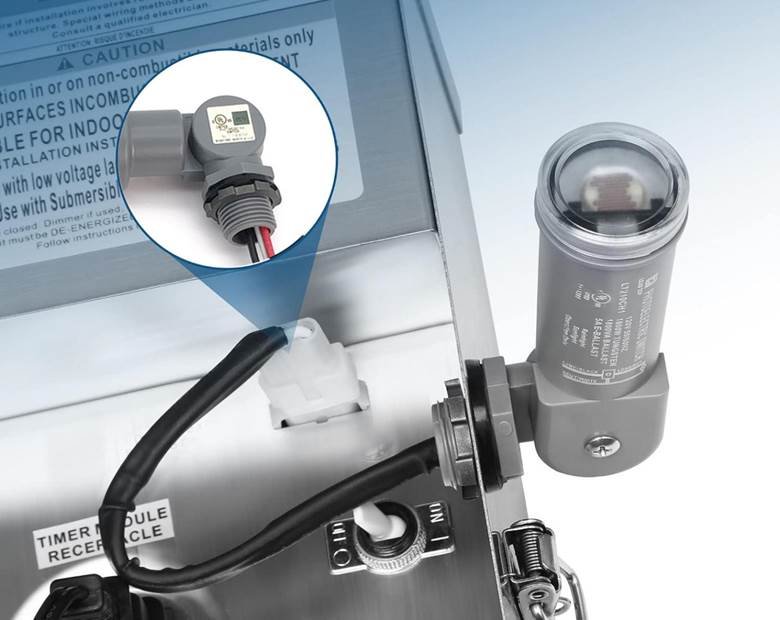
A. Photocells (Light Sensors)
Working Principle:
A photocell, also known as a photoresistor or light-dependent resistor (LDR), changes its resistance based on the amount of light it is exposed to. The resistance decreases as light intensity increases, and vice versa.

Advantages:
Energy Efficiency: Automatically adjusts lighting based on natural light changes, achieving energy savings and emission reduction.
Automated Control: Adjusts lighting brightness automatically based on environmental light, improving operational efficiency.
Extended Lifespan of Fixtures: Intelligent control reduces the frequency of using fixtures, extending their lifespan.
Applications:
Widely used in public areas light, street lights, and parking lots lights: Photocells ensure reduced brightness during abundant sunlight, enhancing nighttime energy efficiency.
B. Infrared Sensors
Outdoor Applications:
In outdoor environments, infrared sensors are used to monitor human activity, widely applied in security lighting, road lighting, automatic doors, and more.
Advantages:
Energy Saving: Infrared sensors can automatically turn off lighting when not in use, improving safety while achieving energy savings.
Security Monitoring: Outdoor sensors contribute to intelligent home security systems, detecting external activity and triggering timely alarms or security measures.
Access Control: Outdoor sensors can integrate into access control systems, ensuring smart access control where only authorized individuals can unlock doors.
Automatic Door Lighting: During nighttime, outdoor sensors can detect approaching pedestrians, automatically illuminating entrance lights, enhancing home entrance safety.
Energy Management: Outdoor sensors contribute to energy management, automatically turning off external lighting when no one is outdoors, reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
Scenario Linkage: Information from outdoor sensors can be linked with other smart devices. For instance, detecting intrusion can trigger video recording, notify homeowners, or activate alarm systems.
C. Sound Sensors
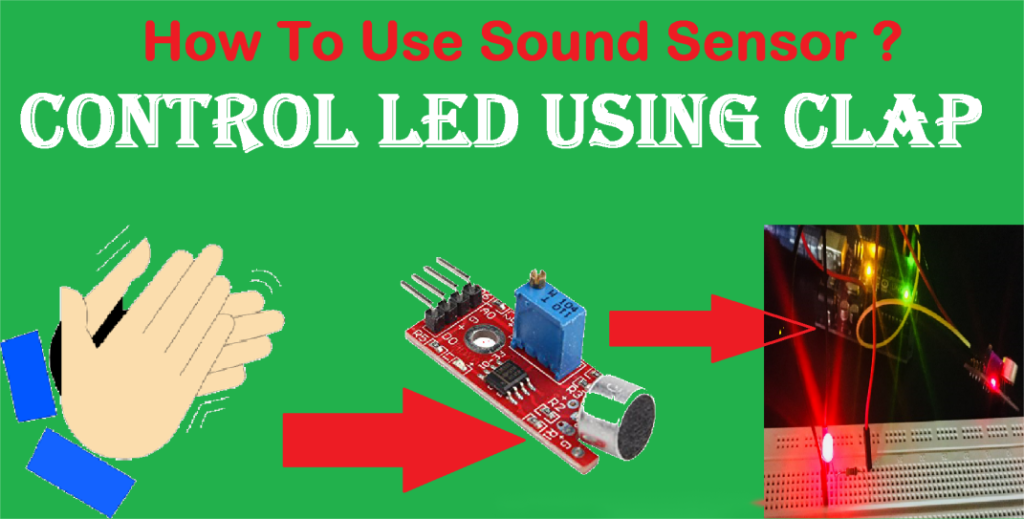
Working Principle:
Sound-activated switches use built-in sound sensors to capture ambient sound. After signal processing and sound recognition, the switch is triggered when a specific sound pattern is detected, automatically controlling lighting devices.
Advantages:
Wide Application: Sound-activated switches are widely used in home automation systems, lighting control in public places, medical equipment, etc.
Convenience: Users can easily control devices with their voice, improving daily life and work efficiency.
Energy Efficiency: Sound-activated switches have the advantage of environmental friendliness and energy saving, reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, indoor and outdoor sensors enhance the convenience, safety, and energy management levels of smart homes through intelligent monitoring and control.







